CSEE Colloquium
Computational Brain Connectivity Using Diffusion MRI
Ҫağatay Demiralp
Brown University
1:30pm Tuesday, 18 September 2012, ITE 325B
In my talk, I’ll present examples from modeling, visualization, and analysis of diffusion-derived structural brain connectivity. I’ll first introduce two interactive visual analysis tools that use novel planar representations of the brain. I’ll show that two-dimensional map representations that are viewed, interacted with, and enriched like online geographical maps result in faster and more accurate exploration of brain connectivity.
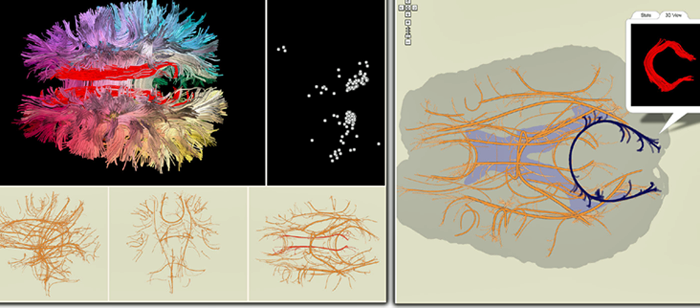
Second, I’ll introduce neural tract-based probability density functions, including joint densities of tract arc length and scalar diffusivity measures, as biomarkers. I’ll demonstrate their simple and effective use in detecting individual and group differences. I’ll also describe a new coherence measure for neural tract clusters based on geometric slicing. I’ll show that a refinement of neural tract clustering based on this measure leads to a significant improvement in clustering results that is not possible directly using standard methods.
Third, I’ll describe a new coloring method for three-dimensional line fields based on Boy's real projective plane immersion. This coloring method is smooth and one-to-one, except on a set of measure zero. I’ll demonstrate its use in visualization of neural tracts and cross-sectional diffusion MRI brain images.
Çağatay Demiralp is a PhD candidate in computer science at Brown University. His research interests are in characterizing patterned structures in data both qualitatively and quantitatively using topological, geometric as well as statistical approaches. While computational brain connectivity using diffusion MRI has been the focus of his thesis research, he has published on a diverse set of topics ranging from surface deformation to semantic segmentation. He received Brown University’s Brain Sciences Research award, IEEE Vis Best Poster award, and ASSH Best Layout and Best Scientific Presentation awards.